Reforestation, afforestation and deforestation – three different terms that are becoming more and more popular, as the world discusses issues related to climate change and wildlife conservation.
But what exactly do they mean and where are the differences?
Table of Contents
What is Deforestation?

Simply speaking, deforestation is the removal of a forest or a stand of trees for a number of different purposes.
80% of tropical deforestation is caused by agriculture.
Other causes of deforestation are our high demand for forest products, such as furniture or paper, mining and oil extraction, as well as infrastructure development.
Due to industrialization and a constant growth of population, deforestation has massively increased within the last decades.
About 2.000 years ago, 80% of Western Europe was forested; today the figure is sobering 34%.
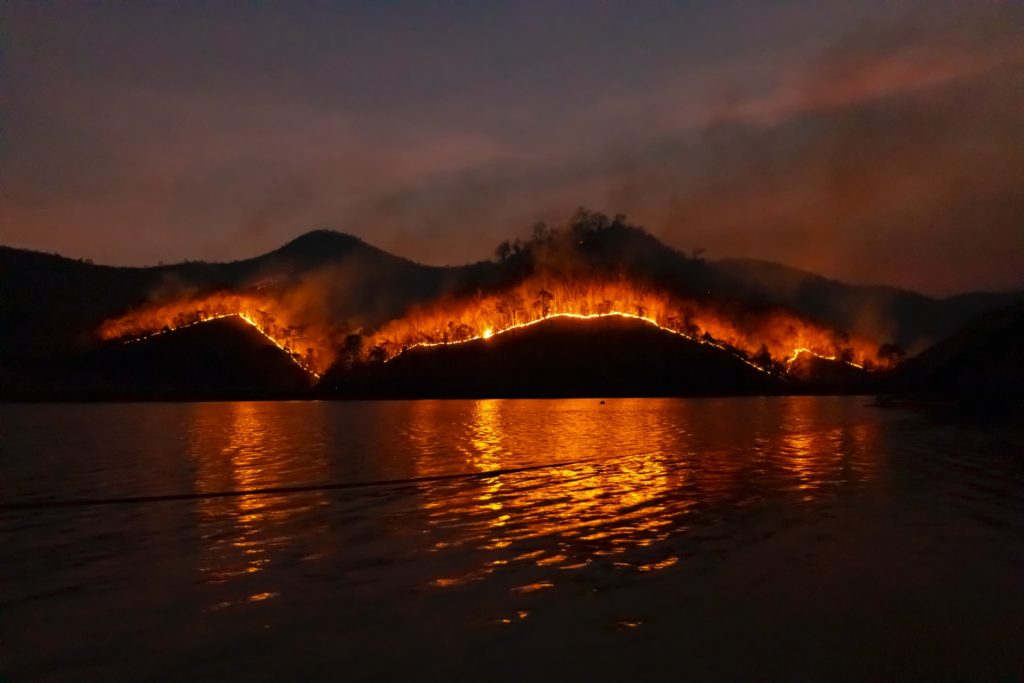
As a way to clear forested land for other purposes, each year, millions of acres of forest around the world are destroyed or degraded by fire.
This practice is also known as slash-and-burn agriculture and and very unsustainable. When the cleared plot becomes infertile after a while, the farmers move to a new fresh plot and repeat the practice.
Watch: Why slash-and-burn fires in Indonesia are so harmful
The most concentrated deforestation caused by us humans occurs in tropical rainforests.
According to the following map published by the World Wildlife Fund (WWF), the hot spots are located in the Amazon, the Atlantic Forest and Gran Chaco, Borneo, the Cerrado, Choco-Darien, the Congo Basin, East Africa, Eastern Australia, Greater Mekong, New Guinea, and Sumatra.

What Causes Deforestation?
The list of causes of deforestation is long. Here are some of the most common reasons why forests are destroyed today:
Agriculture
The rising population numbers on our planet lead to a higher demand for food and other daily life items – and so the need for agricultural products grows.
Especially commodities such as palm oil and soybeans are produced on a large scale. They not only play a big part in out diet, but are also found in countless other products, for example animal feed and cosmetics.
One of the major problems about this is that the destruction is irreversible. Even when efforts are made to replenish barren plantations, the depleted soil is not able to produce biodiversity like it used to.
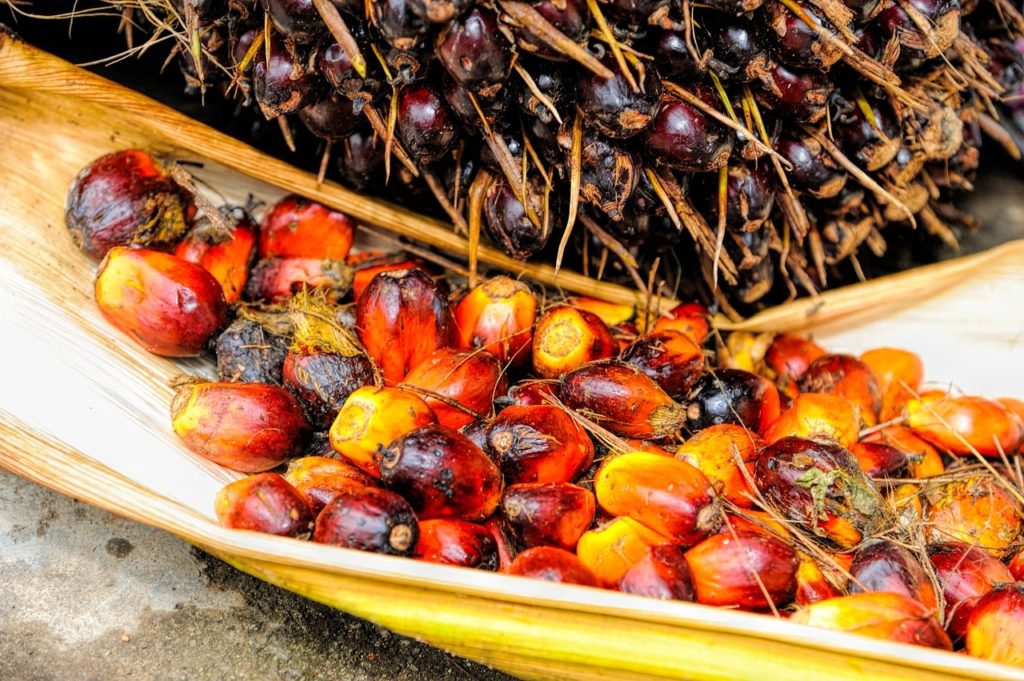

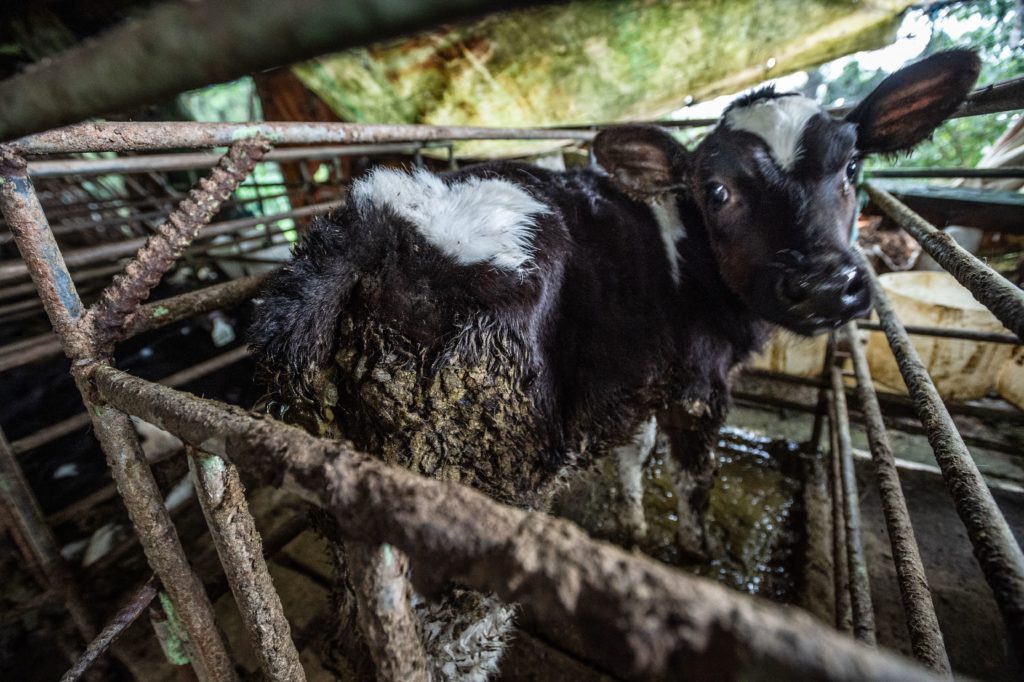
Livestock Farming
Livestock farming requires a lot of land and causes extensive deforestation worldwide. Today, 70% of cleared lands in the Amazon are used as cattle pastures.
An estimated 58.4% of the Amazon rainforest is in Brazil. The country is home to 215 million cows grazing on 162 million hectares (or 19% of its land mass). It is the largest exporter in the world, supplying about one quarter of the global market.
The deforestation caused by cattle ranching alone is responsible for the release of 340 million tons of carbon to the atmosphere every year.

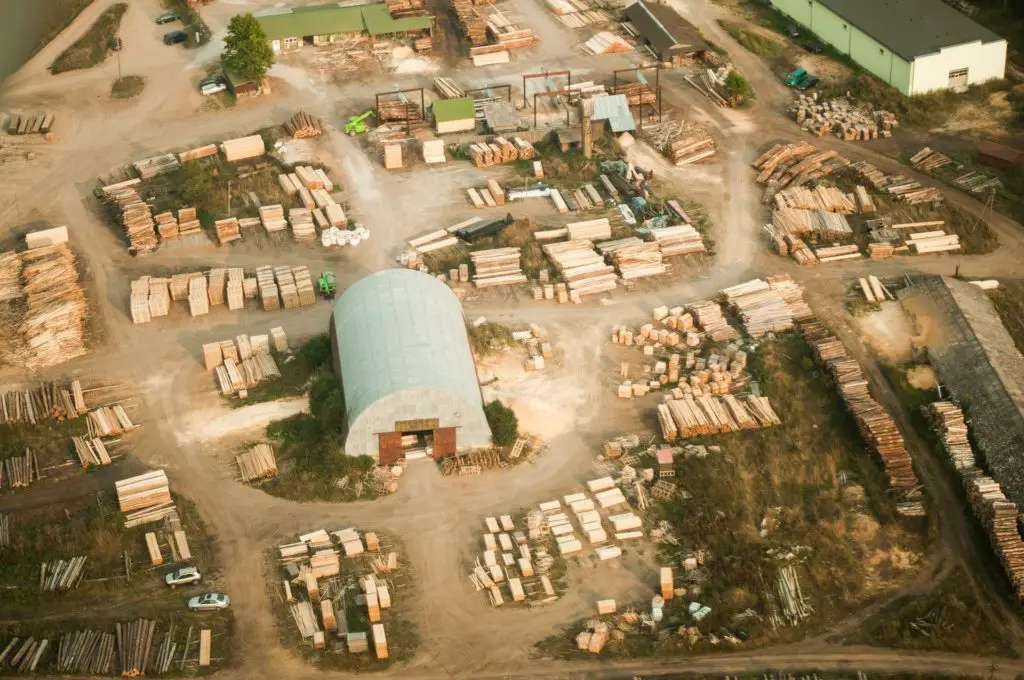
Unsustainable Logging:
Did you know that Indonesia is one of the largest exporters of timber, with about 80 percent of it being exported illegally? The country was even named the “Fastest Forest Destroyer,” in the 2008 Guinness World Records!
Illegal logging often takes place in countries with poor governance and law enforcement capacity.
Legislation in consumer markets like the US, the EU, Australia, and Japan, such as the Lacey Act in the US, have led to reductions in the volume of illegal timber imports into those countries.
However, other emerging markets, such as China, Vietnam, and India have been less focused on sustainability issues. China for example has become a significant market for timber, accounting for half of global illegal timber imports.

Infrastructure
Logging, both legal and illegal, often follows road expansion, because infrastructure development allows access to previously remote (and often unclaimed) land.
This is a good example for simultaneous and sequential causes of deforestation, which is almost always the case.
The need for extensive infrastructure will only increase with time and dams, roads, railways, canals, ports, pipelines and mines are potentially a major cause of future forest loss.

Climate Change
Extreme weather events cause massive destruction of forests worldwide each year. With the progression of of global warming, those events occur more often and in higher intensity.
More deforestation means an increase in climate change, which increases the chances of the vegetation drying out, which in turn increases the risk of fire and so on.

Causes of deforestation in a nutshell to download:

What are Disadvantages of Deforestation?
Forests are home to 80% of terrestrial biodiversity, containing a wide array of trees, plants, animals and microbes. It comes as no surprise that deforestation has a variety of devastating consequences.
Increased Greenhouse Gases
Healthy forests absorb carbon dioxide, preventing them from accumulating in the atmosphere and warming our planet.
The lack of trees allows a greater amount of greenhouse gases to be in the atmosphere.
Plus, when trees are felled, all the carbon they’ve been storing is released.
Loss of forests contributes as much as 10 percent of global greenhouse-gas emissions each year.

Destruction of Homelands
According to the United Nations, indigenous people are spread across 90 countries, with 5,000 distinct cultures and 4,000 unique languages. Millions of them live in tropical forests.
With their precious knowledge about rainforests, as well as their spiritual relationships to the natural world, indigenous tribes are protectors of 80 percent of the most biodiverse areas on Earth!
Watch: Amazon rainforest indigenous people in fight for survival- BBC News
It should be our priority to protect them, their cultures and their homelands. A study published in the journal PNAS concluded that most effective way to protect the Amazon rainforest might be to leave it in the hands of its indigenous residents.
Instead, as the forests are destroyed or degraded, indigenous people are forced to change their resource base. Deforestation is leaving whole groups with nowhere to go.
Sign Now: Survival International's Petition to Stop Brazil's Genocide

Soil Erosion and Flooding
In the last 150 years, half of the topsoil on the planet has been lost. Madagascar for example, loses so much soil to erosion that its rivers run red, staining the surrounding Indian Ocean. Astronauts have remarked that it looks like Madagascar is bleeding into the sea.
Watch: Satellite shows extent of terrible destruction to the planet - BBC
The results are loss of fertile land, increased pollution and sedimentation in streams and rivers, eventually causing declines in fish and other species.
Plus, degraded lands are also often less able to hold onto water, which can worsen flooding.

Extinction of Species
According to recent estimates, the world is losing 137 species of plants, animals and insects every day to deforestation. That’s 50,000 species each year.
How does deforestation cause species extinction?
Trees create shelter and provide a place for animals to feed, nest, breed and hide from predators. A declining number of trees means that the forest will be unable to support a large population of species. As population sizes shrink, so does the genetic variation, which will eventually lead to the extinction of a species.
As of December 2019, a total of 20.334 tree species had been included in the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species, of which 8.056 were assessed as globally threatened.

Habitat Loss
Several countries, including Indonesia, India, the Philippines, Thailand, Burma, Bangladesh, Malaysia, China, Sri Lanka, Laos, Nigeria, Rwanda, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Kenya, Liberia, Guinea, Ghana Ivory Coast, Guatemala, Mexico and Honduras have lost between 30 to 50 percent of their forest cover within a century.
Animals that heavily rely on trees may be unable to adapt to a new habitat.
Read more: What is the Goal of Wildlife Conservation?

Read more on deforestation in this report published by the WWF.
Afforestation and Deforestation
Reforestation, afforestation and deforestation are often used in the same context. We know now that deforestation is the removal of a forest or a stand of trees. So, what do reforestation and afforestation mean?
What is Afforestation?
Afforestation and deforestation are two opposite practices. Afforestation refers to the process of planting trees in an area that does not have trees naturally in order to create a forest.
Importance of Afforestation
The following graphic shows the global afforestation and deforestation numbers over the last thirty years.
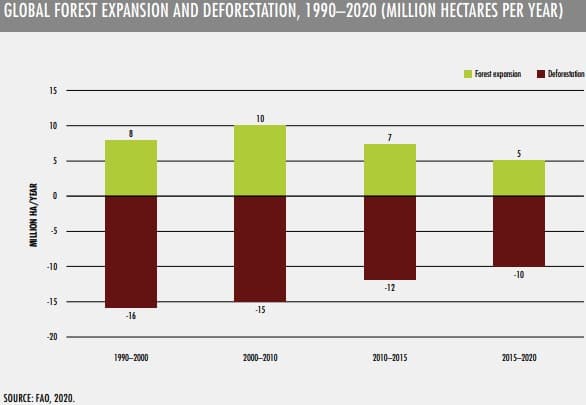
It’s pretty obvious that we are in need of more trees in order to counterbalance reforestation levels.
But why are trees so important?
Advantages of Afforestation
Trees are important for a number of reasons. As you might have guessed, the main advantages of afforestation are closely related to the disadvantages of deforestation.
Wildlife Protection
While deforestation causes habitat loss for the world’s wildlife, afforestation can aid in protecting animals and plants.
By restoring natural habitats, we give them a chance to relocate in order to maintain the natural balance between the local flora and fauna and us humans.

Prevention of Soil Erosion
Barren lands can get badly affected by flooding, which causes soil erosions.
Tree roots on the other hand hold the soil together, helping to produce fertile farmland and making sure that landslides are avoided.
Water Storage
Trees are masters at storing rainwater. In a world where water is the most precious resource, it is crucial that they are protected.
Especially in regions that suffer from water scarcity, the local population relies on a certain minimum level of groundwater which can be uses as drinking water.

Improved Air Quality
Worldwide in major cities and generally in the countries with the worst air quality, people suffer from air-related conditions.
The reason for that is simple: Along with the deforestation levels, our production of carbon dioxide has increased in the last few decades.
Trees on the other hand purify carbon dioxide and offer oxygen through photosynthesis. The more trees there are, the fresher the air we breathe.
Stabilizing the Climate
Global warming has many causes, one of them being deforestation.
Afforestation efforts can help to stabilize the climate by converting semiarid lands into forests. The planted trees will absorb CO2, store carbon and release oxygen back into the atmosphere.
This process helps to slow down global warming, which is caused by air pollutants absorbing sunlight and solar radiation that have bounced off the earth’s surface.

Economic Opportunities
Planting trees requires workers. Thus, afforestation can provide employment, especially to poorer communities.
What is the Difference between Afforestation and Reforestation?
While afforestation and deforestation are opposites, afforestation and reforestation are closely related. Yet, they don’t mean the same thing. Reforestation refers to the process of replanting an area with trees.
In other words, reforestation means the restocking of existing forests, afforestation is the creation of a forest in an area that never used to have trees.
Will Planting Trees Save The Planet?
Planting trees is latest seemingly flawless (and totally Instagrammable) trend for everyone who cares about the environment (and don’t we all?).
Travelers volunteer, all kinds of brands promote their sustainable practices by promising a certain amount of trees planted per product sold, and the coolest birthday present for the green thinkers among us seems to be a certificate sold by a non-profit organization in exchange for a planted tree somewhere in the world.
So far so good, how can you go wrong with planting trees?, is what you are thinking now? Well, unfortunately it’s not that simple. Scientists have warned that planting all those trees could potentially cause more harm than good.
Tree planting became really popular in 2019, when a study published in the journal Science claimed that planting a trillion trees could capture more than a third of all the greenhouse gases that have been released into the atmosphere since the Industrial Revolution.
It received lots of criticism by several scientists who argued that the huge number of trees could harm ecosystems, make wildfires worse, and even exacerbate global warming.
How exactly? Let’s have a look at the disadvantages of afforestation.
Disadvantages of Afforestation
If not practiced properly, afforestation has the potential to cause several severe issues.
Location
Remember, afforestation and reforestation are not the same thing. Planting forests in areas that never used to be covered with trees can result in far-reaching problems.
Replacing a snowy area with a forest for example, could even lead to an increase in global warming. The reason for that is that the surface of the trees is darker than the white snow, which reflects much more of the sun’s energy.
Similarly, dry and hot areas, such as Africa’s Savannah, aren’t necessarily a good place for afforestation efforts.
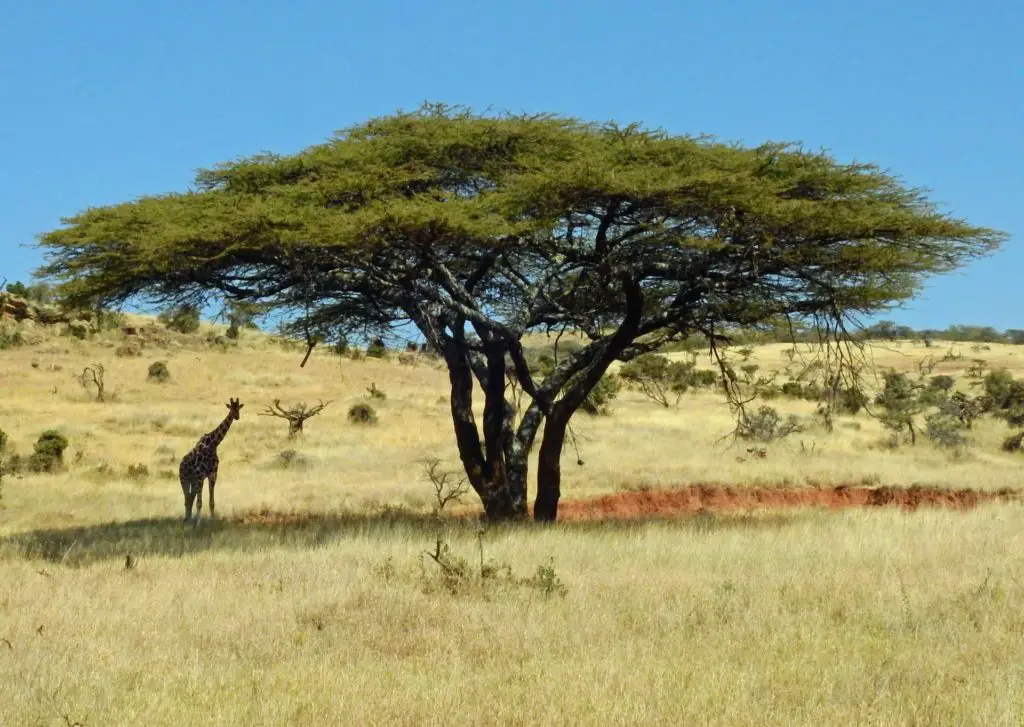

Biodiversity
The ancient grasslands and savannas are home to millions of animals and contain immense biodiversity. Replacing them with trees destroys plant and animal habitat.
Read: 15 Endangered Animals in Africa
Plus, grasslands are known to be great carbon sinks!
Local Communities
Tress, with their deep roots, use up lots of water — leaving less for other species, including humans. That threatens communities who rely on livestock forage and groundwater recharge in their homelands.
Moreover, in the Miombo woodlands in Zambia, Mozambique, and Tanzania, wood fuels are used as a renewable energy source by millions of people. Afforestation projects in those areas that don’t include the local population might leave them without alternative energy sources.
Distraction
While reforestation efforts are important for the protection of our forests, other issues shouldn’t be overlooked. For example, replacing fossil fuels with renewable energy sources like solar power, is crucial for a sustainable future.
Tree planting initiatives – especially the ones that have big names behind them – tend to distract from other problems that get less attention.
When it comes to the global discussions on tree-planting and climate change, local scientists often claim to be sidelined.
For example, several African scientists argue that woodland policies in Southern Africa are forced on to them from institutions such as the World Bank, the Food and Agriculture Organization, the International Union for Conservation of Nature and others.
Read more: The trouble with indiscriminate tree-planting in Africa - Mail & Guardian
How Can We Stop Deforestation?
Forests already only cover 31% of the planet’s surface. Unless drastic measures are taken to protect them from further denudation, it is predicted that this number will reduce to 10% by the year 2030.
What can we do to stop that process?
How To Save The Trees
There are a few things you can do to protect our forests.
Go Vegan
The benefits of being vegan are endless. And while the connection between your diet and our world’s forests does not seem logical for everyone at first glance, it is so simple: By not buying animal products, you automatically stop supporting deforestation for livestock farming.


Buy Forest-Friendly
Pam oil, found in 40-50 percent of household products, contributes to 300 football-field-sized swaths of rainforest being cut down every hour. Inform yourself which products and brands use palm oil and find forest-friendly alternatives.
Donate
Donating a little bit of money for a good cause is always a good idea. Remember, every penny counts. Just make sure that the organization is trustworthy.


Spread the Word
Talk, write, and share, with your grandparents, neighbors, children and Facebook friends (is that still a thing?). The more people are aware of the problem and the possible solutions, the better!
Plant Trees
… but only where it makes sense.
Again, just because there are disadvantages of afforestation, that doesn’t mean that supporting the right reforestation projects is not important!

I hope you have a better overview of reforestation, afforestation and deforestation, the problems they can cause and the solutions they can provide now. If you have any questions or comments, let us know below!
